End-to-end supply chain management in the Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) industry refers to the integrated coordination of all processes involved in moving products from raw material sourcing to final delivery at retail shelves or directly to consumers. Given the highly competitive and fast-paced nature of FMCG, efficient supply chain management is crucial for meeting consumer demand, reducing costs, ensuring product quality, and maintaining brand loyalty.
What is End-to-End Supply Chain Management?
End-to-end supply chain management (E2E SCM) is a comprehensive approach that oversees the entire journey of a product, from the initial sourcing of raw materials to the final delivery and even post-sale services. It emphasizes the integration and coordination of all supply chain functions to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Here's a more detailed breakdown:
Key aspects of End-to-End Supply Chain Management:
-
Holistic View: E2E SCM takes a comprehensive view of the entire supply chain, rather than treating each stage as a separate entity.
-
Integration: It focuses on integrating all supply chain activities, such as procurement, manufacturing, logistics, and distribution, to ensure a seamless flow of goods and information.
-
Visibility and Control: E2E SCM enhances visibility and control over the entire supply chain, allowing companies to track goods, monitor their condition, and identify potential issues or bottlenecks.
-
Optimized Processes: By integrating and coordinating all functions, E2E SCM aims to optimize the entire supply chain process, leading to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
-
Focus on Customer Experience: E2E SCM extends beyond the physical movement of goods to include post-sale services and customer feedback, ensuring a positive customer experience.
Benefits of End-to-End Supply Chain Management:
-
Increased Efficiency: By streamlining processes and eliminating redundancies, E2E SCM can significantly improve efficiency across the entire supply chain.
-
Reduced Costs: Improved efficiency and optimized operations can lead to lower costs in areas like inventory management, transportation, and warehousing.
-
Enhanced Visibility: E2E SCM provides real-time visibility into the supply chain, allowing companies to respond quickly to disruptions and make informed decisions.
-
Improved Customer Satisfaction: By ensuring timely delivery, accurate order fulfillment, and responsive post-sale support, E2E SCM can significantly improve customer satisfaction.
-
Better Decision Making: With access to comprehensive data and real-time insights, companies can make more informed decisions about inventory management, production planning, and resource allocation.
Why is End-to-End SCM Crucial in the FMCG sector?
End-to-end supply chain management (SCM) is crucial in the Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) sector because it streamlines processes, reduces costs, and improves customer satisfaction. By managing the entire supply chain from raw materials to delivery, FMCG companies can enhance efficiency, minimize risks, and ultimately boost profitability.
Here's why end-to-end SCM is essential for FMCG:
-
Cost Reduction: End-to-end SCM helps reduce costs by automating manual tasks, optimizing inventory, and streamlining logistics. For example, better demand forecasting can minimize overstocking and stockouts, while efficient logistics can reduce shipping errors and delays.
-
Increased Efficiency: Streamlining processes across the entire supply chain, from procurement to delivery, leads to faster response times and improved operational efficiency. This allows FMCG companies to quickly adapt to changing customer demands and market trends.
-
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: End-to-end SCM improves customer satisfaction by ensuring timely deliveries, accurate product information, and a seamless purchasing experience. Real-time visibility into the supply chain allows for better communication and proactive issue resolution.
-
Risk Mitigation: By providing end-to-end visibility, end-to-end SCM helps identify and mitigate potential risks such as supply disruptions, quality issues, or regulatory non-compliance. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of disruptions on business operations and brand reputation.
-
Improved Supplier Relationships: End-to-end SCM fosters stronger relationships with suppliers by promoting transparency, collaboration, and mutual understanding of supply chain needs. This leads to better coordination, improved product quality, and more reliable supply.
-
Competitive Advantage: By optimizing the supply chain, FMCG companies can gain a competitive advantage through lower costs, faster delivery times, and enhanced customer satisfaction. This allows them to effectively compete in the fast-paced FMCG market.
Components of Supply Chain Management in FMCG 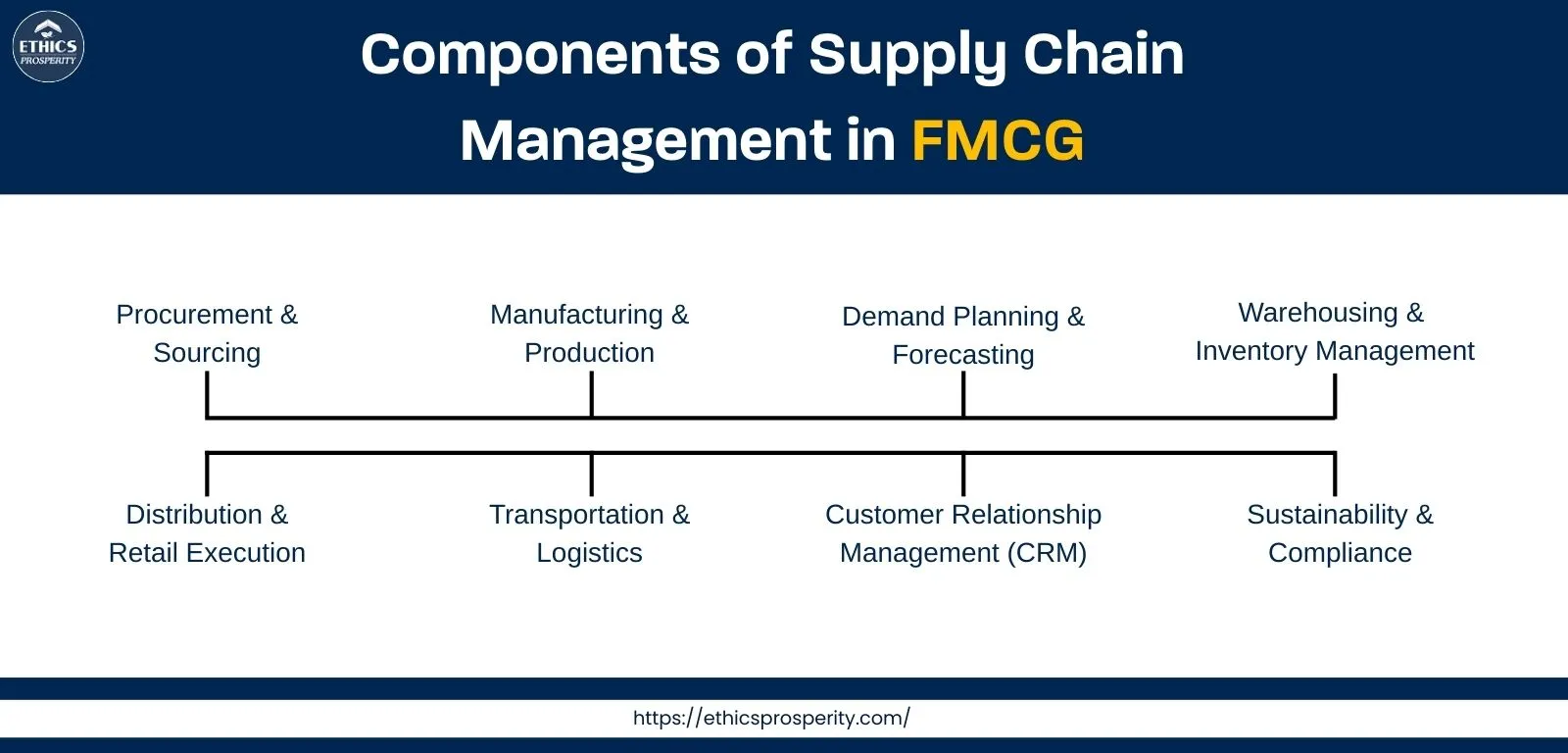
-
Procurement & Sourcing
-
Identifying and acquiring raw materials, packaging, and other inputs.
-
Building strong vendor relationships to ensure cost efficiency and quality.
-
Manufacturing & Production
-
Converting raw materials into finished goods at scale.
-
Ensuring compliance with quality, hygiene, and safety standards.
-
Optimizing production planning to balance demand and capacity.
-
Demand Planning & Forecasting
-
Using data analytics, AI, and machine learning to predict demand patterns.
-
Aligning supply with seasonal peaks, promotions, and consumer trends.
-
Warehousing & Inventory Management
-
Storing finished goods in strategic locations close to demand centers.
-
Using Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) to monitor stock levels.
-
Ensuring accurate forecasting to avoid overstocking or stockouts.
-
Distribution & Retail Execution
-
Ensuring wide product availability through distributors, retailers, and modern trade.
- Strengthening omnichannel strategies (offline + e-commerce).
- Managing order fulfillment, demand fluctuations, and last-mile delivery challenges.
-
Transportation & Logistics
-
Moving goods from factories to distribution centers, wholesalers, and retailers.
-
Leveraging multi-modal transport (road, rail, air) for cost and time efficiency.
-
Using technology like GPS and route optimization for faster deliveries.
-
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
-
Tracking consumer preferences, feedback, and buying behavior.
-
Ensuring faster response to complaints, returns, or quality issues.
-
Sustainability & Compliance
-
Reducing carbon footprint, packaging waste, and energy consumption.
-
Meeting regulatory standards for environment, labor, and product safety
Technology-Driven Transformation in FMCG Supply Chain Management
The FMCG supply chain is evolving rapidly, with technology emerging as the backbone of efficiency, agility, and resilience. From predictive analytics to real-time visibility, digital solutions are transforming every stage of the supply chain, enabling businesses to meet rising consumer expectations and market volatility.
Key Technology Enablers:
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML)
-
Enhances demand forecasting accuracy.
-
Automates decision-making in inventory and logistics planning.
-
Internet of Things (IoT) & RFID
-
Enables real-time product tracking across warehouses and transit.
-
Improves traceability, especially for perishables.
-
Blockchain Technology
-
Builds trust through transparent, tamper-proof supply chain records.
-
Facilitates compliance and ethical sourcing verification.
-
Robotics & Automation
-
Streamlines warehouse operations with robotic picking and packing.
-
Reduces human error and boosts operational speed.
-
Big Data & Advanced Analytics
-
Provides end-to-end visibility for performance monitoring.
-
Identifies inefficiencies and optimizes resource allocation.
-
Cloud Computing & Digital Platforms
-
Enhances collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers.
-
Supports scalability and flexibility in operations.
-
Sustainability Tech Solutions
-
Smart packaging and eco-friendly logistics reduce environmental impact.
-
Carbon footprint monitoring tools aid in achieving ESG goals.
Challenges in End-to-End Supply Chain Management for FMCG 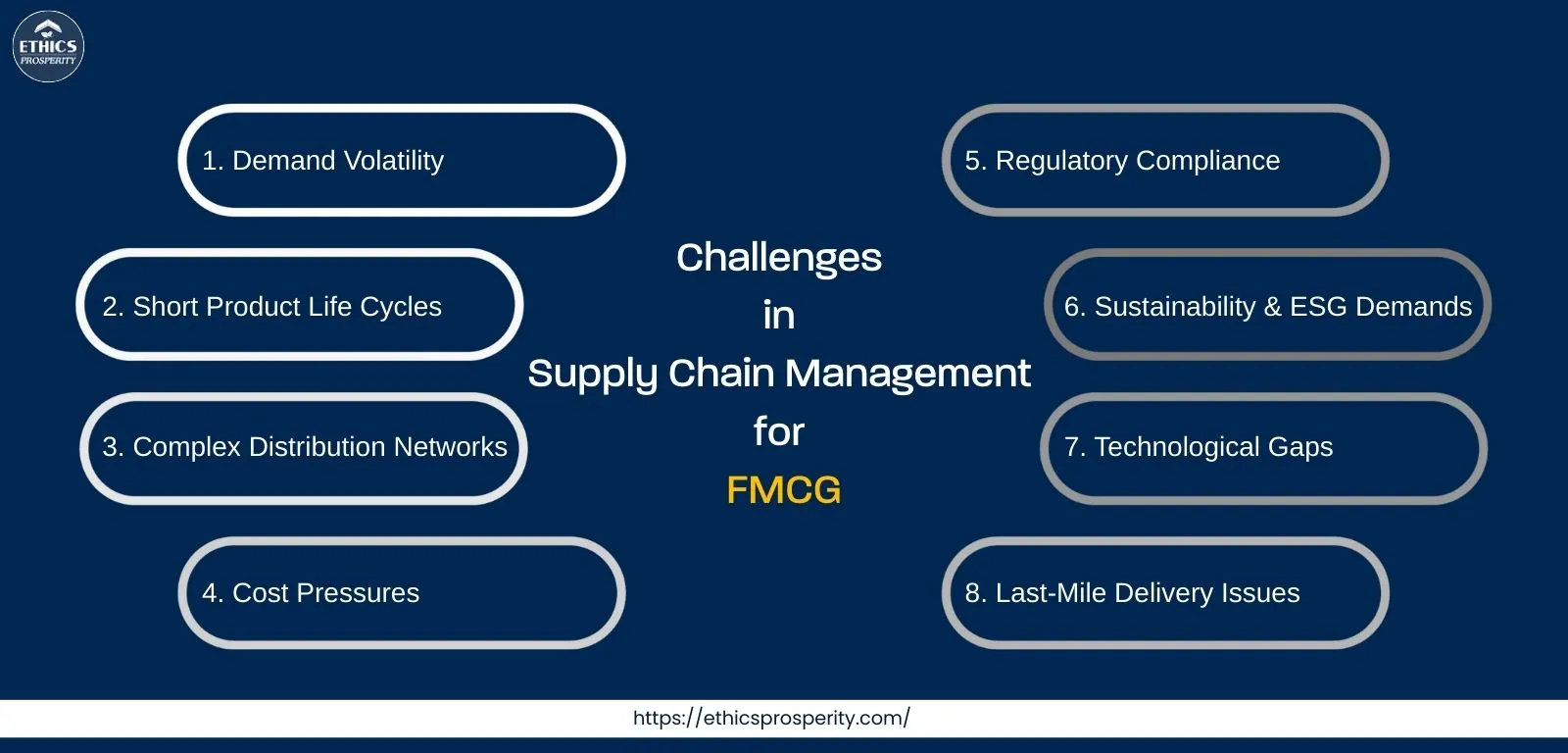
Managing supply chains in the FMCG sector is complex due to the high demand variability, product perishability, and the need for wide distribution. Companies must overcome several challenges to maintain efficiency and competitiveness:
1. Demand Volatility
-
Consumer preferences shift rapidly, influenced by trends, promotions, and seasonality.
-
Inaccurate forecasting can lead to overstocking or stockouts.
2. Short Product Life Cycles
-
FMCG products often have limited shelf life.
-
Managing freshness, especially for perishable goods, requires efficient inventory turnover.
3. Complex Distribution Networks
-
FMCG relies on multilayered networks (distributors, wholesalers, retailers, e-commerce).
-
Ensuring product availability across urban and rural markets is challenging.
4. Cost Pressures
-
Rising fuel, labor, and logistics costs strain margins.
-
Competitive pricing in FMCG limits the ability to pass costs to consumers.
5. Regulatory Compliance
-
Strict food safety, labeling, and sustainability regulations must be followed.
-
Non-compliance can damage brand reputation and invite penalties.
6. Sustainability & ESG Demands
-
Growing consumer and regulatory focus on eco-friendly packaging, ethical sourcing, and carbon footprint reduction.
-
Balancing sustainability with cost-efficiency is a constant challenge.
7. Technological Gaps
-
Many FMCG players, especially in emerging markets, lack advanced digital infrastructure.
-
Fragmented systems hinder real-time visibility and coordination.
8. Last-Mile Delivery Issues
-
Fast delivery expectations, especially with e-commerce growth, strain logistics networks.
-
Reaching remote or rural areas adds additional complexity.
Future Trends in FMCG Supply Chain
The FMCG supply chain is entering a new era where speed, transparency, and sustainability are no longer negotiable. Companies are embracing innovation to stay competitive and meet the evolving needs of both retailers and consumers. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Digital-First Supply Chains
-
End-to-end digital integration using AI, IoT, and blockchain for real-time visibility.
-
Cloud-based platforms enable faster decision-making and collaboration.
2. Hyper-Personalization & Demand Sensing
-
AI-driven demand sensing to capture changing consumer behaviors.
-
Tailored product assortments and delivery models for different markets.
3. E-Commerce & Omnichannel Growth
-
Greater emphasis on direct-to-consumer (D2C) models.
-
Seamless integration between online, offline, and quick-commerce channels.
4. Automation & Smart Warehousing
-
Use of robotics, drones, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) for faster fulfillment.
-
Smart warehouses powered by AI and predictive analytics.
5. Sustainable & Circular Supply Chains
-
Eco-friendly packaging and green logistics are gaining priority.
-
Circular models focusing on recycling, reusability, and waste reduction.
6. Resilience & Risk Management
-
Focus on building agile, resilient supply chains to mitigate disruptions (pandemics, geopolitical issues, climate change).
-
Diversified sourcing and nearshoring strategies to reduce dependency on single markets.
7. Data-Driven Decision Making
-
Advanced analytics and big data are helping optimize inventory, pricing, and distribution.
-
Predictive insights improve efficiency and reduce operational risks.
In the fast-paced FMCG sector, where consumer expectations are constantly evolving, end-to-end supply chain management is no longer just a competitive advantage—it is a necessity. By integrating processes across procurement, production, warehousing, logistics, and last-mile delivery, businesses can achieve greater efficiency, visibility, and resilience. Companies that embrace digital tools, real-time data insights, and collaborative ecosystems are better positioned to reduce costs, optimize inventory, and respond swiftly to market shifts.
At Ethics Prosperity, we empower FMCG brands to build agile, transparent, and customer-centric supply chains that not only drive operational excellence but also support long-term growth. The future belongs to organizations that can seamlessly connect every link in their supply chain—and with the right partner, that future can start today.





