In today’s highly dynamic supply chain ecosystem, inventory replenishment is the foundation of consistent product availability and customer satisfaction.
It ensures that warehouses, stores, and fulfillment centers maintain optimal stock levels without overstocking or stockouts.
For B2B organizations, efficient replenishment in supply chain operations drive smoother logistics flows, optimized capital utilization, and sustainable growth. Businesses like Ethics Prosperity—a leading provider of End-to-End Supply Chain Management solutions—integrate smart replenishment strategies across global operations to achieve operational agility and resilience.
What Is Inventory Replenishment?
Inventory Replenishment is the critical process of restocking products by moving goods through the supply chain, ensuring stock levels are maintained to meet anticipated demand. It is how businesses guarantee the necessary product is available precisely when and where customers need it—whether at a retail shelf, a fulfillment center, or a dedicated staging area. This process is fundamentally about moving inventory based on demand forecasts, stock thresholds, and consumption patterns, transitioning from reactive to proactive execution.
The function operates at two crucial levels:
-
Macro-level: Replenishing Distribution Centers (DCs) from manufacturing plants or external vendors.
-
Micro-level (Internal): The Warehouse replenishment system that dynamically moves stock from reserve locations to active picking areas within the warehouse.
The success of Replenishment in Supply Chain is defined by its ability to:
-
Minimize inventory holding costs.
-
Virtually eliminate stockouts.
-
Maximize customer service reliability.
Modern warehouse replenishment systems now leverage automation, analytics, and demand forecasting in supply chain to eliminate manual guesswork, prevent costly delays, and significantly improve working capital efficiency.
Why Is Inventory Replenishment Important?
Effective stock replenishment goes far beyond restocking shelves. It directly impacts revenue, operations, and customer loyalty.
Key Benefits:
-
Avoid Stockouts: Maintain consistent product availability to prevent sales loss.
-
Reduce Overstocking: Lower carrying costs by keeping optimal stock levels.
-
Enhance Forecast Accuracy: Improve data-driven decision-making with demand sensing solutions.
-
Boost Warehouse Productivity: Streamline internal movements using Warehouse Management Systems (WMS).
-
Enable Scalability: Support multiple SKUs and e-commerce channels through integrated planning.
In industries like FMCG, retail, and manufacturing, inventory replenishment aligns procurement, warehousing, and last-mile delivery—ensuring every link of the supply chain operates in harmony.
Components of an Effective Replenishment Strategy
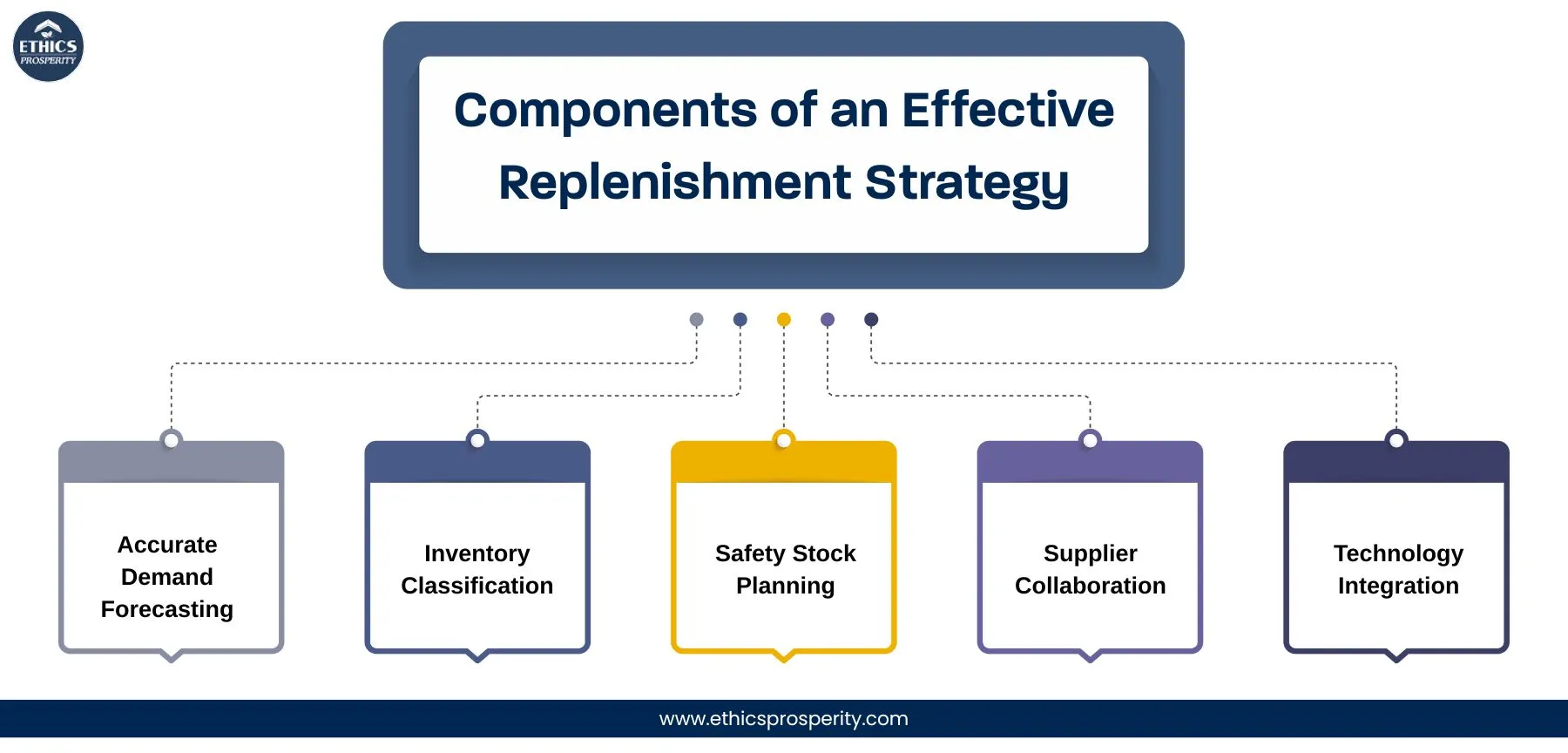
1. Accurate Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting in supply chain operations uses historical data, seasonality, and market analytics to predict future sales.
AI and ML-powered models help identify fluctuations early, allowing companies to plan replenishment cycles efficiently.
2. Inventory Classification
Classify inventory using models like ABC analysis to prioritize high-value items.
This enables smarter allocation of space and replenishment frequency.
3. Safety Stock Planning
Establish safety stock buffers to mitigate risks from supplier delays, market volatility, or transportation disruptions.
4. Supplier Collaboration
Engage in vendor-managed inventory (VMI) systems and data-sharing networks for smoother coordination and on-time delivery.
5. Technology Integration
Implement automation and IoT-enabled tools such as Blockchain in Smart Warehousing to monitor stock levels in real time and enhance visibility across inbound and outbound logistics.
Types of Inventory Replenishment Methods
1. Periodic Replenishment
Inventory is reviewed at regular intervals, and restocking is done based on time schedules rather than current demand.
Useful for stable demand environments but less adaptive to fluctuations.
2. Reorder Point Replenishment
Replenishment triggers automatically when inventory hits a pre-set threshold.
This model ensures a balance between holding costs and service levels.
3. Demand-Driven Replenishment
Powered by AI, IoT, and predictive analytics, this approach adapts to real-time market signals, sales velocity, and customer behavior.
It’s widely used by Quick Commerce Companies and omni-channel retailers.
4. Hybrid Model
Combines the flexibility of demand-driven systems with the stability of time-based cycles for businesses with complex supply chains or multi-location networks.
Inventory Replenishment Process: Step-by-Step
-
Data Collection: Aggregate real-time data from POS, ERP, and WMS systems.
-
Demand Analysis: Forecast requirements using demand sensing and analytics.
-
Reorder Trigger: Establish reorder points based on minimum stock levels.
-
Procurement Coordination: Engage suppliers through automated purchase orders.
-
Inbound Logistics: Plan transportation and receiving schedules efficiently.
-
Warehouse Allocation: Assign stock to optimal zones using slotting strategies.
-
Distribution & Last-Mile Delivery: Move replenished stock to retail or customer nodes.
Each step plays a role in achieving seamless End-to-End Supply Chain Management and ensuring business continuity even under fluctuating market conditions.
Technology in Inventory Replenishment
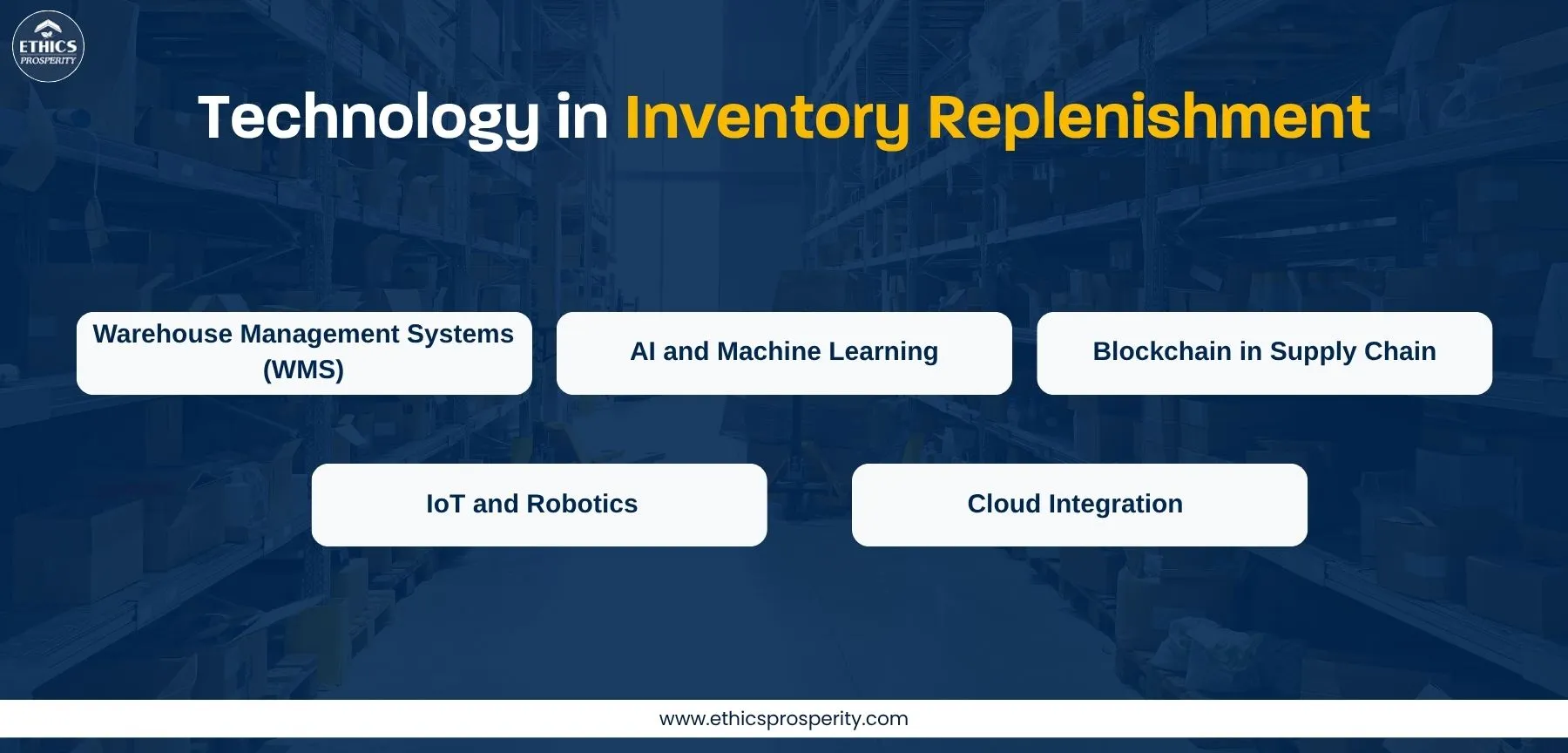
Technology is redefining how companies handle stock replenishment and inventory optimization.
1. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
A WMS automates the replenishment process through real-time tracking, barcode scanning, and intelligent allocation of goods within warehouses.
2. AI and Machine Learning
AI models continuously analyze sales patterns, weather data, and promotional impacts to predict demand with higher accuracy.
3. Blockchain in Supply Chain
Blockchain enhances transparency and trust by ensuring that every inventory transaction is immutable, traceable, and secure.
It’s particularly useful for high-value industries like pharma, automotive, and electronics.
4. IoT and Robotics
Smart sensors track shelf levels automatically, while robotics handle material movement, improving accuracy and reducing human error.
5. Cloud Integration
Cloud-based supply chain solutions allow stakeholders to monitor inventory across regions, warehouses, and 3PL partners simultaneously.
Challenges in Inventory Replenishment
-
Inaccurate Forecasting: Poor data quality leads to excess inventory or lost sales.
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: Unpredictable logistics events can delay replenishment.
-
Lack of Integration: Disconnected ERP and WMS systems limit visibility and responsiveness.
-
Rising Transportation Costs: Affect inbound logistics and reverse supply chain planning.
-
Regulatory Compliance: In sectors like pharma and food, compliance delays can halt restocking.
Companies must leverage data-driven decision-making and real-time monitoring tools to overcome these challenges efficiently.
Conclusion
In today’s competitive marketplace, successful inventory management isn’t about storing products—it’s about timing, precision, and intelligence.
Inventory replenishment acts as the central nervous system of modern warehouse and logistics networks, ensuring every unit flows seamlessly from supplier to shelf.
Organizations adopting digital-first, data-led strategies are experiencing remarkable gains in accuracy, efficiency, and cost reduction.
With innovators like Ethics Prosperity, companies can unlock next-generation capabilities in custom warehousing, demand forecasting, and smart replenishment systems, creating a truly connected, resilient supply chain.


