Distribution Management is a crucial element in running a successful business, playing a key role in supply chain distribution, logistics and distribution, and overall operational efficiency. It focuses on moving products from where they are manufactured to the places where customers can easily purchase them. To increase business profitability, companies must strengthen both sales and distribution strategies while ensuring effective warehouse distribution. In this article, we will explore what distribution management is, along with its key advantages, importance, and the challenges businesses often face.
What is Distribution Management in Supply Chain?
Distribution management in the supply chain refers to the planning, coordination, and control of how products move from manufacturers or warehouse distribution centers to distributors, retailers, and end customers. It ensures that goods reach the right place, at the right time, in the right quantity, and at the lowest cost. Effective supply chain distribution relies on strong logistics and distribution processes, including transportation, inventory planning, and order fulfillment. A well-designed distribution strategy helps create a smooth, efficient, and customer-focused flow of products across the entire supply chain.
Why Is Distribution Management Important?
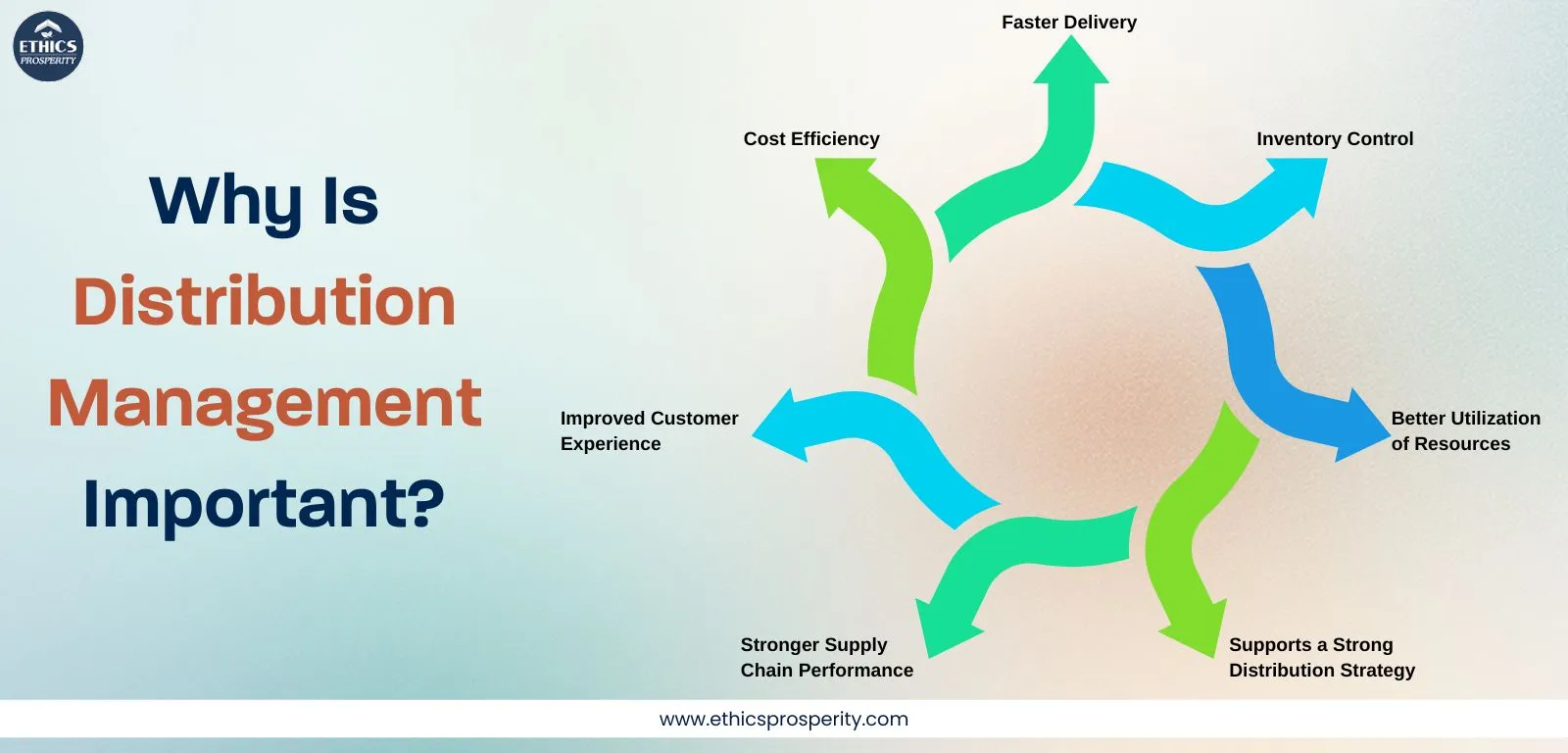
Distribution management is a key business challenge that must be handled well for steady growth. Early delivery of raw materials can lead to damage or extra costs, while late delivery of finished goods can result in lost sales. A strong, data-driven distribution strategy ensures efficient coordination across logistics, warehousing, and delivery to keep the supply chain running smoothly. Its importance lies in:
-
Cost Efficiency – Optimizes transportation, storage, and handling, reducing overall supply chain costs.
-
Faster Delivery – Ensures timely product movement, improving customer satisfaction and competitive advantage.
-
Inventory Control – Helps maintain the right stock levels, reducing shortages and excess inventory.
-
Better Utilization of Resources – Improves the use of warehouses, transportation, and labor.
-
Stronger Supply Chain Performance – Enhances coordination across suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors.
-
Supports a Strong Distribution Strategy – Aligns logistics, warehousing, and delivery processes with business goals.
-
Improved Customer Experience – Ensures accuracy, reliability, and consistency in product availability.
The Distribution Management Process
The distribution management process includes all the steps involved in moving products from manufacturers to end customers. Its key components are:
|
Component |
Primary Function |
Key Benefit |
Technology Used |
|
Inventory Management |
Stock level optimization |
20-30% cost reduction |
RFID, Barcode scanning |
|
Order Processing |
Workflow automation |
40% fewer errors |
CRM integration, APIs |
|
Warehousing |
Strategic storage & operations |
15-20% shipping cost reduction |
WMS, Automated sorting |
|
Transportation |
Route & carrier optimization |
10-15% cost savings |
TMS, Real-time tracking |
|
Customer Service |
Communication & support |
25-30% satisfaction increase |
Integrated customer systems |
Benefits of Effective Distribution Management
Adopting a comprehensive distribution management system delivers measurable gains in operational performance, customer satisfaction, and competitive positioning. Modernizing logistics and distribution, including warehouse distribution, inventory control, and transportation, typically allows companies to recover their investment within 12 to 18 months, while strengthening overall supply chain distribution and supporting a more effective distribution strategy. Some of its benefits are:
-
Reduces overall costs by improving distribution management and streamlining logistics and distribution activities.
-
Ensures faster and more reliable deliveries, strengthening supply chain distribution efficiency.
-
Enhances inventory accuracy and supports smoother warehouse distribution processes.
-
Improves visibility and coordination across the supply chain for better decision-making.
-
Boosts customer satisfaction through consistent product availability.
-
Provides a competitive edge supported by a well-designed distribution strategy.
Distribution Management Strategies
Understanding distribution channels and choosing the right strategic approach are fundamental to effective distribution management. The channel you select shapes customer reach, operational costs, and competitive positioning across supply chain distribution, influencing logistics and distribution, warehouse distribution, and your overall distribution strategy. Some of its strategies are:
-
Centralized Distribution: Consolidates inventory in one main warehouse to reduce storage costs and streamline supply chain distribution.
-
Decentralized Distribution: Uses multiple warehouse distribution points to ensure faster deliveries and improved customer reach.
-
Cross-Docking: Moves products directly from inbound to outbound transport with minimal storage, improving logistics and distribution efficiency.
-
Just-in-Time (JIT) Distribution: Reduces inventory levels by aligning deliveries closely with actual demand.
-
Omnichannel Distribution: Integrates online, offline, retail, and wholesale channels for a unified customer experience.
-
Third-Party Logistics (3PL): Outsources warehousing, transportation, and fulfillment to specialized logistics partners.
-
Real-Time Data and Automation: Uses analytics, tracking systems, and automation to optimize routes, inventory, and overall distribution strategy.
What Are the 4 Channels of Distribution?
The four main distribution channels describe how a product moves from the manufacturer to the final consumer:
-
Direct Channel: The manufacturer sells directly to the customer without intermediaries.
Example: company websites, direct sales teams. -
Indirect Channel – One Intermediary: Involves one middleman, usually a retailer.
Example: manufacturer → retailer → customer. -
Indirect Channel – Two Intermediaries: Involves both a wholesaler and a retailer.
Example: manufacturer → wholesaler → retailer → customer. -
Indirect Channel – Three Intermediaries: Includes an agent in addition to a wholesaler and retailer, helpful for large markets.
Example: manufacturer → agent → wholesaler → retailer → customer.
Challenges in Distribution Management
To achieve effective distribution management, businesses must proactively address its key challenges to ensure a smooth and efficient process. Some of its challenges are:
-
Complex Supply Chain Coordination: Managing multiple suppliers, distributors, and transportation partners makes it difficult to maintain smooth logistics and distribution flow.
-
Inventory Inaccuracies: Overstocking leads to higher carrying costs, while understocking causes delays and lost sales, affecting overall supply chain distribution.
-
Rising Transportation Costs: Fuel prices, driver shortages, and route inefficiencies increase expenses and disrupt delivery schedules.
-
Warehouse Management Issues: Inefficient warehouse distribution processes such as poor layout, slow picking, and outdated systems reduce productivity.
-
Demand Forecasting Errors: Inaccurate forecasts make it challenging to balance stock levels and meet consumer expectations.
-
Limited Visibility Across the Supply Chain: Lack of real-time data makes it hard to track shipments, monitor inventory, and respond quickly to disruptions.
-
Technology Integration Problems: Integrating new systems into existing distribution strategy frameworks can be expensive and time-consuming.
Future Trends in Distribution Management
The following emerging trends in distribution management can help businesses strengthen their operations and position themselves for long-term success in a rapidly evolving market landscape:
-
Automation and Robotics: Increased use of automated picking, packing, and sorting systems will make warehouse distribution faster and more accurate.
-
AI-Driven Decision Making: Artificial intelligence will optimize demand forecasting, route planning, inventory management, and overall logistics and distribution efficiency.
-
Real-Time Supply Chain Visibility: IoT sensors, RFID, and tracking tools will provide end-to-end visibility, enabling quicker responses to disruptions.
-
Sustainable Distribution Practices: Companies will adopt eco-friendly packaging, electric vehicles, and energy-efficient warehouses to reduce carbon footprints.
-
Omnichannel Distribution Models: Seamless coordination across online, offline, retail, and wholesale channels will become essential for meeting customer expectations.
-
Last-Mile Delivery Innovation: Drone deliveries, micro-fulfillment centers, and smart lockers will enhance speed and convenience.
-
Data-Driven Distribution Strategy: Advanced analytics will help companies plan smarter routes, optimize warehouse distribution, and improve supply chain distribution accuracy.
-
Greater Adoption of 3PL and 4PL Services: Businesses will increasingly rely on logistics partners for specialized, scalable distribution management solutions.
Conclusion
Effective distribution management has become essential for businesses aiming to stay competitive in today’s fast-moving market. By strengthening logistics and distribution, enhancing supply chain distribution, and optimizing warehouse distribution processes, companies can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver a stronger customer experience. A well-designed distribution strategy not only streamlines operations but also ensures that products move seamlessly from manufacturers to end customers.
At Ethics Prosperity, we understand the importance of building smarter, data-driven distribution systems that support long-term business growth. By embracing modern tools, real-time visibility, and strategic planning across all areas of distribution management, businesses can position themselves for sustained success in an increasingly dynamic supply chain landscape.
