As someone who has navigated the supply chain landscape for nearly five decades, I can tell you that the difference between merely managing a warehouse and mastering smart warehousing is the difference between surviving and leading. We've moved past the era where a warehouse was just a fixed cost and a four-wall storage unit; today, it is a dynamic, intelligent nerve center powered by data and automation.
For any executive in the B2B sector, understanding this evolution is non-negotiable. Smart warehousing in supply chain is the strategic pivot that determines speed, cost-efficiency, and, ultimately, market dominance.
What is Smart Warehousing?
At its core, smart warehousing is the practice of leveraging advanced technologies—such as Artificial Intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and warehouse robotics—to automate, optimize, and connect every operational layer of a distribution facility. It transforms the passive storage function into an active, decision-making engine.
This is not simply about adding a few pieces of equipment; it's about creating a digitally synchronized system where every asset, product, and process communicates in real-time. This level of synchronization is essential for Warehouse Companies in India looking to maintain a competitive edge in one of the world's most rapidly expanding markets.
The Critical Role in End-to-End Supply Chain Management
Smart warehousing plays a critical role in End-to-End Supply Chain Management by ensuring:
-
Faster order fulfillment cycles
-
Optimized inbound and outbound logistics
-
Reduced human error through robotics
-
Real-time visibility of stock across multiple locations
-
Seamless integration with transportation, procurement, and customer delivery systems
It acts as the nerve center of a modern supply chain, connecting production, storage, and logistics in one intelligent network.
Key Technologies Driving Smart Warehousing
The backbone of smart warehousing is the integrated application of several technologies. As a strategic head, you must view these as investments in business intelligence, not merely hardware purchases.
1. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
A robust Warehouse Management System (WMS) is the operating system of the smart warehouse. It orchestrates all activities, from receiving and putaway to picking and shipping. Modern WMS solutions are cloud-based and use sophisticated algorithms to guide tasks, ensuring the highest level of resource optimization. Without an advanced WMS, the remaining technologies are just expensive toys; with it, they become a cohesive, high-performance machine. The best systems can even integrate with emerging technologies like Blockchain in smart warehousing for immutable transaction logs and enhanced security.
2. Robotics and Automation
Warehouse robotics is one of the most visible forms of warehouse automation. This includes Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) that handle the heavy, repetitive, and often dangerous tasks of moving inventory. Robotics dramatically increases throughput and accuracy, while simultaneously reducing labor costs and workplace injuries. The investment pays for itself through 24/7 operational capability and reduced mis-picks.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML)
AI in logistics is what makes the warehouse 'smart,' not just 'automated.' AI and ML algorithms analyze vast datasets—historical order fulfillment data, seasonal trends, and even external factors like weather—to provide predictive optimization.
-
Dynamic Slotting: AI determines the optimal storage location for every SKU based on predicted demand and picking routes.
-
Predictive Maintenance: ML models analyze the performance of machinery, such as conveyors and warehouse robotics, to predict failures before they happen, moving maintenance from reactive to preventative.
4. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT sensors and devices connect the physical world to the digital WMS. Every piece of equipment, every pallet, and every shelf can be fitted with sensors that monitor location, temperature, humidity, and even vibration. This provides the 'Enhanced Visibility' necessary for true control. For operations involving sensitive goods, such as cold chain or pharmaceutical logistics, IoT ensures the strict compliance required for Custom Warehousing and specialized storage.
5. Data Analytics
Raw data is useless; actionable data is power. Smart warehousing employs advanced data analytics to interpret the massive streams of information generated by the WMS, robotics, and IoT devices. This data drives Key Performance Indicator (KPI) dashboards that allow supply chain leaders to identify bottlenecks, measure true cost-to-serve, and continually refine processes for maximum efficiency.
How Smart Warehousing Works
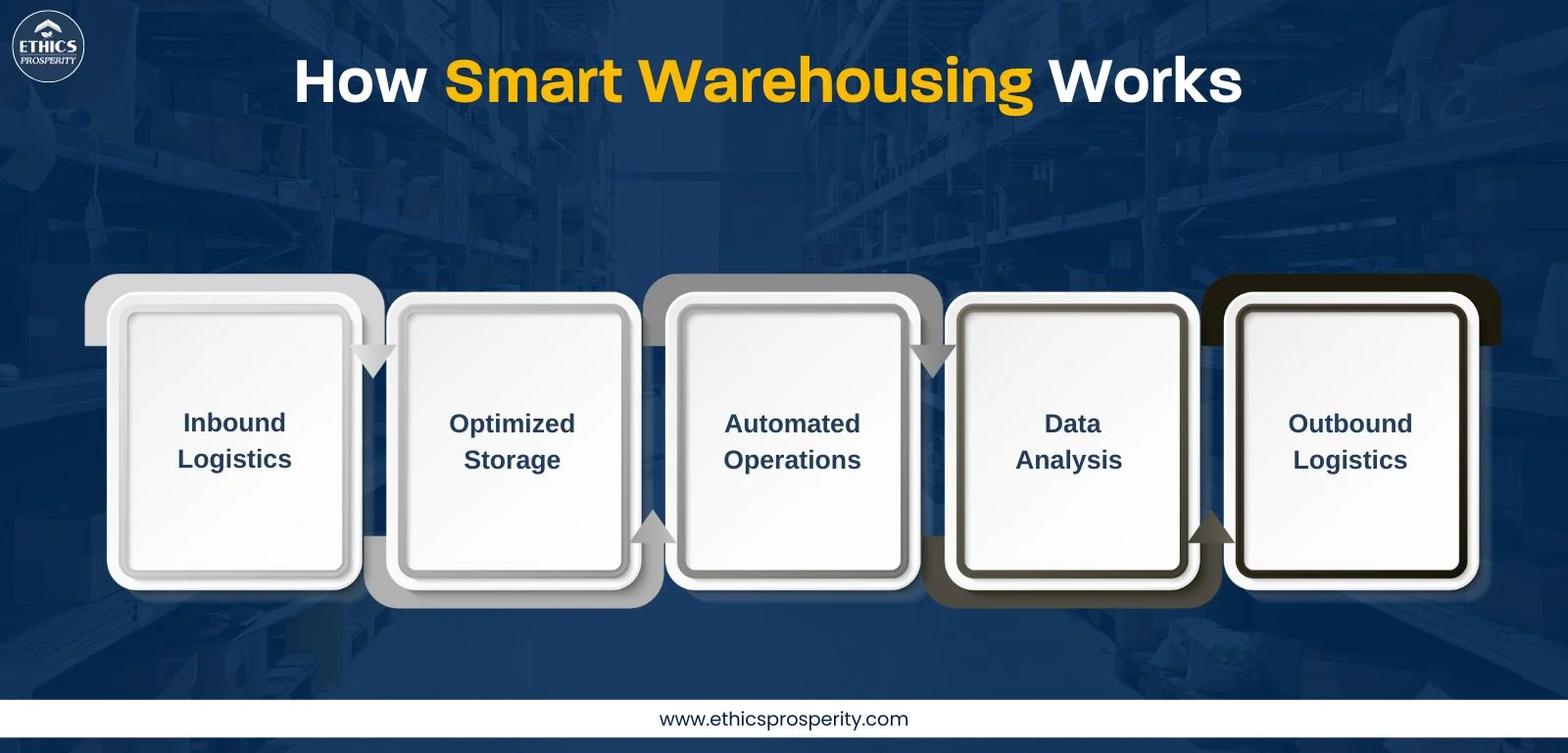
A veteran knows that execution is everything. Here is the operational flow of a truly smart warehouse:
1. Inbound Logistics
-
Automated Scheduling: The WMS integrates with carrier management systems to schedule precise delivery windows, optimizing dock utilization. Shipments often arrive via part Truck load (PTL) to maximize space efficiency during transit.
-
Rapid Receiving: Goods, whether raw materials or finished products, are received and immediately scanned using automated vision systems or RFID. This minimizes the time inventory spends sitting on the receiving dock, instantly feeding real-time stock levels into the WMS.
2. Optimized Storage
-
AI-Driven Putaway: Based on the product's velocity, size, and weight, the AI system determines the optimal storage location. Faster-moving items are placed closest to the picking and packing stations (the 'golden zone').
-
Vertical Space Utilization: Warehouse robotics and automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) allow for denser, safer, and higher stacking, maximizing the cubic capacity of the facility.
3. Automated Operations
-
Goods-to-Person (G2P): Instead of workers walking aisles (person-to-goods), warehouse robotics move the required inventory directly to the picking station. This is the ultimate form of warehouse automation, dramatically boosting picking speed and accuracy.
-
Dynamic Order Consolidation: As orders are fulfilled, the WMS directs them through automated conveyance and sortation systems, ensuring they are consolidated for the most cost-effective and timely dispatch.
4. Data Analysis
-
Real-Time Benchmarking: The system continuously monitors operational metrics against benchmarks, flagging deviations immediately. This allows for swift intervention before a small issue escalates into a major disruption. This level of precise data is crucial for Supply Chain Companies in India operating across vast geographic areas.
5. Outbound Logistics
-
Seamless Handover: Completed orders are automatically labeled and sorted for the correct carrier and route. This final process is crucial for minimizing the Last Mile Delivery cost and time.
-
Direct Integration with Carriers: The WMS communicates directly with Last Mile Delivery Companies and other transport providers, ensuring that the truck waiting at the dock is loaded immediately, often having been pre-loaded with the most appropriate part Truck load configuration.
Benefits of Smart Warehousing
The transition to smart warehousing provides a powerful competitive advantage that resonates through the entire organization, delivering a compelling B2B value proposition.
1. Increased Efficiency & Speed
Automation eliminates manual processes, allowing operations to run 24/7. This speed is non-negotiable in the modern era, particularly with the rise of Quick Commerce Companies. The difference between Quick commerce vs e-commerce fulfillment often comes down to the speed enabled by smart, automated systems. The reduced latency in processing orders translates directly to faster market access.
2. Reduced Costs
While the initial investment in warehouse automation is high, the long-term operational savings are immense. Costs are reduced through:
-
Labor Optimization: Moving workers to higher-value, supervisory tasks.
-
Space Optimization: Dense storage enabled by warehouse robotics means less real estate is needed.
-
Energy Savings: Smart lighting and AI in logistics-driven climate control.
3. Improved Accuracy
Human error is the leading cause of inaccuracy. Automated scanning, G2P systems, and AI-driven sorting lead to near-perfect picking rates. This improved accuracy not only lowers costs associated with returns (the Reverse Supply Chain ) but also dramatically improves customer satisfaction.
4. Enhanced Flexibility and Scalability
Traditional warehouses are rigid. Smart warehousing solutions, often built on modular and scalable warehouse robotics and cloud-based WMS, allow businesses to rapidly scale capacity up or down to meet fluctuating demand, without the need for large capital construction projects. This is especially relevant for businesses needing temporary or flexible Custom Warehousing solutions.
5. Better Customer Satisfaction
Reliable, fast, and accurate fulfillment—made possible by smart warehousing—is the cornerstone of modern customer loyalty. For B2B clients, meeting a Service Level Agreement (SLA) is paramount, and the smart warehouse ensures those SLAs are met consistently. Furthermore, the ability to rapidly process orders supports the decentralized model of Micro-Fulfillment, which moves inventory closer to the final point of consumption, ensuring ultra-fast delivery times.
Challenges in Implementing Smart Warehousing
No major strategic shift comes without hurdles. From my experience, the primary challenges in adopting smart warehousing are:
-
High Initial Capital Outlay: The cost of implementing a full suite of warehouse robotics, WMS, and IoT infrastructure is substantial. It requires a strong business case and executive commitment.
-
System Integration Complexity: Integrating disparate systems—the WMS, robotics control software, and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)—is technically demanding and prone to failure if not managed by an expert team.
-
Talent Gap: The required workforce shifts from manual labor to specialists in maintenance, data science, and AI in logistics. Retraining and hiring for these roles is a global challenge.
-
Legacy System Blunder: Many established Warehouse Companies in India and globally run on outdated WMS platforms. Migrating from these legacy systems to a modern, cloud-based platform can be a massive, disruptive project.
Future of Smart Warehousing: Trends to Watch
The trajectory of smart warehousing is clear: increasing autonomy, deeper data integration, and total network transparency.
-
Total Autonomy: We are moving toward lights-out operations, where minimal human intervention is required.
-
Predictive Logistics: The integration of AI will extend beyond the four walls, allowing the system to place inventory orders automatically, book part Truck load capacity, and predict regional demand shifts with unprecedented accuracy.
-
Blockchain Adoption: The use of Blockchain in Supply Chain will become standard for transparency and verification. Specifically, Blockchain in smart warehousing provides an unchangeable record of every inventory movement, eliminating disputes and enhancing security.
The future of smart warehousing is the future of the competitive supply chain—a lean, visible, and highly responsive machine designed for speed and Ethics Prosperity. Embracing this transformation is no longer a matter of competitive advantage; it’s a prerequisite for relevance.
Conclusion:
For any B2B organization, the discussion should no longer be if you will adopt smart warehousing, but how and when. The technologies—from warehouse management systems to AI in logistics and warehouse robotics—are mature. The benefits—from cost reduction and improved accuracy to speed and customer satisfaction—are quantifiable.
At Ethics Prosperity, we empower organizations with end-to-end supply chain management solutions — integrating custom warehousing, automation technologies, and real-time visibility to future-proof logistics operations.
To lead your sector, particularly in dynamic environments supported by world-class Supply Chain Companies in India, you must move decisively. The smart warehousing in supply chain strategy you implement today will define your cost structure and market position for the next decade.





