B2B Warehousing & Fulfillment: Meaning, Process, and Key Use Cases
As a supply chain leader with more than four decades of operational experience, I’ve witnessed how B2B warehousing and fulfillment evolved from traditional storage models to technology-driven strategic functions. In today’s competitive landscape, enterprises across FMCG, electronics, pharma, retail, and industrial sectors require scalable warehousing, accurate order fulfillment, and fully integrated logistics solutions—not as an option but as a necessity.
This guide explains everything businesses need to know about B2B warehousing, the fulfillment process, use cases, and how companies can leverage modern technologies such as WMS, automation, AI in supply chain management, Blockchain in smart warehousing, and micro-fulfillment systems to achieve seamless efficiency.
What is B2B Warehousing and Fulfillment?
B2B warehousing refers to storage solutions designed for businesses that ship products in large quantities to wholesalers, distributors, retailers, and other enterprises. Unlike B2C fulfillment, which deals with individual customers, B2B operations involve:
-
Larger order volumes
-
Palletized shipments
-
Strict SLAs
-
Complex compliance requirements
-
Multi-node coordination
B2B fulfillment, on the other hand, covers the end-to-end cycle of handling business orders, including:
-
Receiving inventory
-
Storage & replenishment
-
Order picking
-
Packaging
-
Dispatch
-
Documentation
-
Final delivery to business customers
This model forms the backbone of End-to-End Supply Chain Management, enabling seamless movement of goods from upstream suppliers to downstream distribution networks.
The Importance of B2B Warehousing in Supply Chain
B2B warehousing is a critical foundation of modern supply chain operations for several reasons:
1. Ensures Business Continuity
With industries shifting toward fast replenishment cycles, having a stable storage ecosystem ensures that production and distribution never stop.
2. Supports Large-Scale Operations
Industries like FMCG, automotive, and electronics require bulk movement of goods. B2B warehousing maintains buffer stocks, preventing shortages.
3. Improves Cost Efficiency
Centralized storage reduces fragmented logistics and helps lower transportation, labor, and inventory holding costs.
4. Enhances End-to-End Visibility
With WMS, IoT sensors, and RFID, warehouse operations are now transparent, traceable, and integrated.
5. Enables Scalability
B2B warehouses support expansion into new regions, product categories, and B2B customer groups.
B2B Fulfillment Process Explained
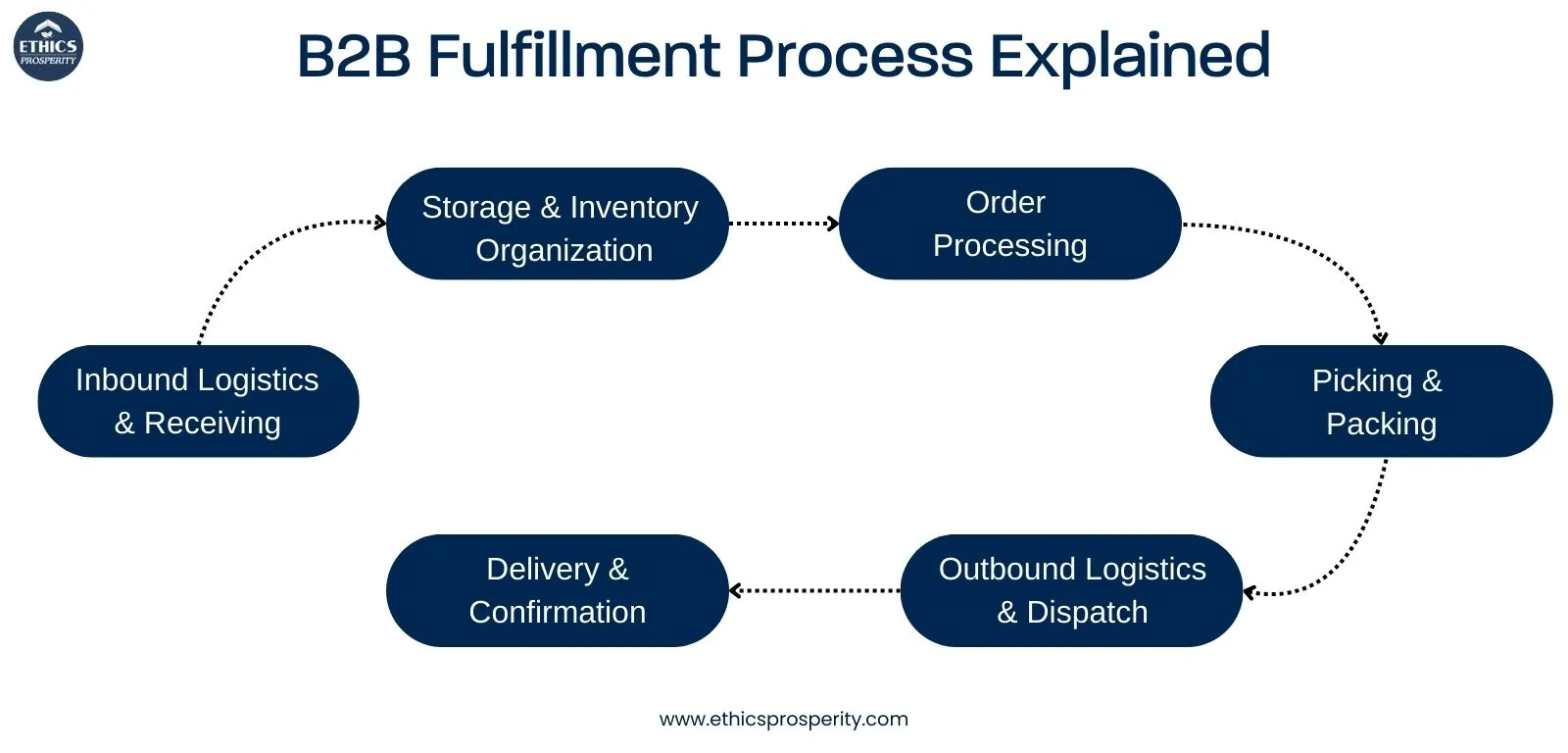
B2B fulfillment process improves operational efficiency, reduces errors, and increases customer satisfaction.
Below is the complete process flow:
1. Inbound Logistics & Receiving
Raw materials or finished goods arrive from domestic or international suppliers. The warehouse team performs:
-
Unloading
-
Document verification
-
GRN creation (Goods Received Note)
-
Quality checks
-
Barcode labeling
This aligns with SCM vs Logistics, ensuring that inbound operations support broader supply chain planning.
2. Storage & Inventory Organization
Inventory is stored based on:
-
SKU velocity
-
Product type
-
Temperature zones
-
Safety stock thresholds
-
FIFO/FEFO requirements
Technologies like Warehouse Management System (WMS) and Blockchain in Supply Chain support accuracy and real-time traceability.
3. Order Processing
B2B orders are received from channels such as:
-
EDI
-
B2B portals
-
ERP systems
-
Vendor applications
-
Distributor platforms
Order validation ensures:
-
Inventory availability
-
Customer-specific SLAs
-
Order grouping
-
Delivery window scheduling
4. Picking & Packing
B2B picking methods include:
-
Zone picking
-
Batch picking
-
Pallet picking
-
Wave picking
Large-volume orders demand precision to avoid stock discrepancies. Packaging includes:
-
Pallet wrapping
-
Cartonization
-
Custom protective packaging
-
Documentation (e.g., invoice, e-way bill)
5. Outbound Logistics & Dispatch
Outbound processes involve:
-
Load planning
-
Route optimization
-
Carrier selection
-
Consolidation
-
Dispatch scanning
Large B2B shipments often use:
-
FTL (Full Truck Load)
-
Rail freight
-
3PL companies in India for last-mile delivery
6. Delivery & Confirmation
Once goods are delivered to retailers, distributors, or wholesalers, proof of delivery is captured through:
-
ePOD
-
GPS tracking
-
TMS systems
This step strengthens Reverse Supply Chain efficiency in case of returns or replacements.
Key Use Cases of B2B Warehousing & Fulfillment
1. FMCG & Grocery Distribution
High-velocity products require fast replenishment cycles and real-time stock visibility.
2. Electronics & Consumer Durables
Sensitive goods demand secure storage and controlled handling.
3. Pharma & Healthcare
Cold storage warehouses maintain temperature compliance (2°C–8°C and –20°C).
4. Industrial & Automotive
Large, heavy, and fast-moving SKUs require pallet racking and mechanized handling.
5. E-commerce & Quick Commerce Companies
Micro-fulfillment centers and dark stores support ultra-fast order cycles.
Benefits of Effective B2B Warehousing & Fulfillment
1. Improved Lead Time
Enterprises report a 20–40% reduction in lead time with optimized warehouse operations.
2. Higher Inventory Accuracy
WMS-driven warehouses achieve 98–99.8% accuracy in stock records.
3. Enhanced Cost Savings
Companies using outsourced logistics save 15–25% on operational costs annually.
4. Faster Fulfillment for Retail / Distributors
Improved order cycle time drives stronger retailer relationships and on-shelf availability.
5. Better Scalability
B2B fulfillment offers easy scaling for seasonal or regional expansions.
How Technology is Transforming B2B Fulfillment
The future of B2B fulfillment is technology-driven. Some critical systems include:
1. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Supports real-time tracking, slotting optimization, replenishment alerts, and cycle counts.
2. Blockchain in Smart Warehousing
Enhances traceability, transparency, and fraud prevention across the supply chain.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI in Supply Chain Management)
AI powers:
-
Demand forecasting
-
Route optimization
-
Inventory planning
-
Automated QC systems
4. Micro-Fulfillment Centers
Located closer to consumption zones, reducing logistics costs by up to 50%.
5. Robotics & Automation
Technologies such as AMRs, conveyor sorting, and robotic picking increase throughput by 30–60%.
Choosing the Right B2B Warehousing Partner
When shortlisting Warehouse Companies in India for B2B operations, evaluate:
1. Infrastructure Capability
-
Racking systems
-
Handling equipment
-
Temperature-controlled zones
2. Technology Expertise
-
WMS, TMS, OMS
-
IoT sensors
-
Blockchain readiness
3. Network Strength
Multi-city hubs improve service radius and reduce lead times.
4. Compliance & Safety
Industry certifications like FSSAI, GMP, HACCP, ISO 9001 & 45001.
5. Scalability & Flexibility
Support for peak seasons and expansion into new markets.
Conclusion
B2B warehousing and fulfillment stand at the core of modern supply chain efficiency. With rising customer expectations, growing omnichannel operations, and the need for optimized logistics solutions, businesses must adopt technology-driven and scalable models.
Platforms like Ethics Prosperity specialize in delivering End-to-End Supply Chain Management, helping enterprises streamline storage, optimize logistics, and enhance supply chain resilience.
